Superior configuration parameters management how your Mac shops cached Apple and iCloud content material. This is how you can change the settings.
Content material caching on macOS controls what iCloud and Apple content material will get saved domestically in macOS while you obtain Apple software program or retailer information in iCloud. It additionally permits caching of different Apple software program comparable to:
- Machine firmware and restoration updates
- macOS installers
- Rosetta updates
- Screensavers and wallpapers
- Screensavers and wallpapers
- Xcode parts
The concept with macOS content material caching is that in the event you obtain Apple software program or information from iCloud, you possibly can permit different Apple units to entry that content material from the unique Mac. All with out having to obtain it once more from the web.
If you use iCloud or obtain software program or information from Apple, a number of the information (content material) will get downloaded and saved domestically in your Mac.
Enabling content material caching
As a way to use content material caching on the Mac, you will need to first allow it in System Settings->Basic->Sharing->Content material Caching.
If you do that, you will get a sheet permitting you to set what content material you need cached: All Content material, Solely Shared Content material, or Solely iCloud Content material.
You can even choose whether or not or not you wish to share your web connection and (in the event you click on the Choices button) the place to retailer the content material cache and the way giant it must be. After you flip content material caching on, you will be prompted to restart your Mac or different units.
By sharing your community connection, you permit iOS units to make use of your Mac’s community connection to entry cached content material – in addition to share content material if these units are tethered through USB.
You may additionally get an alert while you activate content material caching that your different Apple units will “uncover the cached content material over time” – so do not anticipate the opposite units to entry the cache instantly.
It might take just a few seconds for content material caching to start out up as a result of macOS has to launch a background service to handle it.
To show off content material caching, merely flip the swap again to the off place in System Settings->Sharing.
Limitations
In Intro to content material caching within the Apple Platform Deployment information, Apple notes that there are just a few limitations to content material caching – specifically that solely sure sorts of community protocols and handle sorts are allowed:
“You should use content material caching on networks that use community handle translation (NAT) for the content material cache and all units, on networks consisting of publicly routable IP addresses, and optionally for units tethered to a Mac (for instance, when provisioning many units without delay utilizing Apple Configurator). Apple units routinely contact a close-by content material cache with none configuration through the use of a lookup service that maps shopper personal and public IP addresses to configurations registered with Apple from Mac computer systems with content material caching turned on”
Apple additionally recommends that the Mac doing the caching solely has a single wired Ethernet connection to the community for efficiency causes. When you use a WiFi connection for the caching Mac, efficiency could also be affected.
By configuring a Mac on this means, you successfully set it as much as be a content material cache server. Your community is in no way restricted to just one Mac operating content material caching, so you possibly can have a number of cache servers in operation.
Apple has a whole listing of what sorts of content material are cached in Technote 102860 Content material sorts supported by content material caching in macOS.
There are additionally explanations and diagrams of how content material caching works in Intro to content material caching within the Apple Platform Deployment information.
“By default, content material caching is proscribed to a selected subnet, however you possibly can set it to offer content material caching for:
All mixtures of subnets of the native community that share a typical public IP handle,
Any mixture of subnets of publicly accessible IP addresses (with further DNS settings being required)”
The place the cache settings are saved
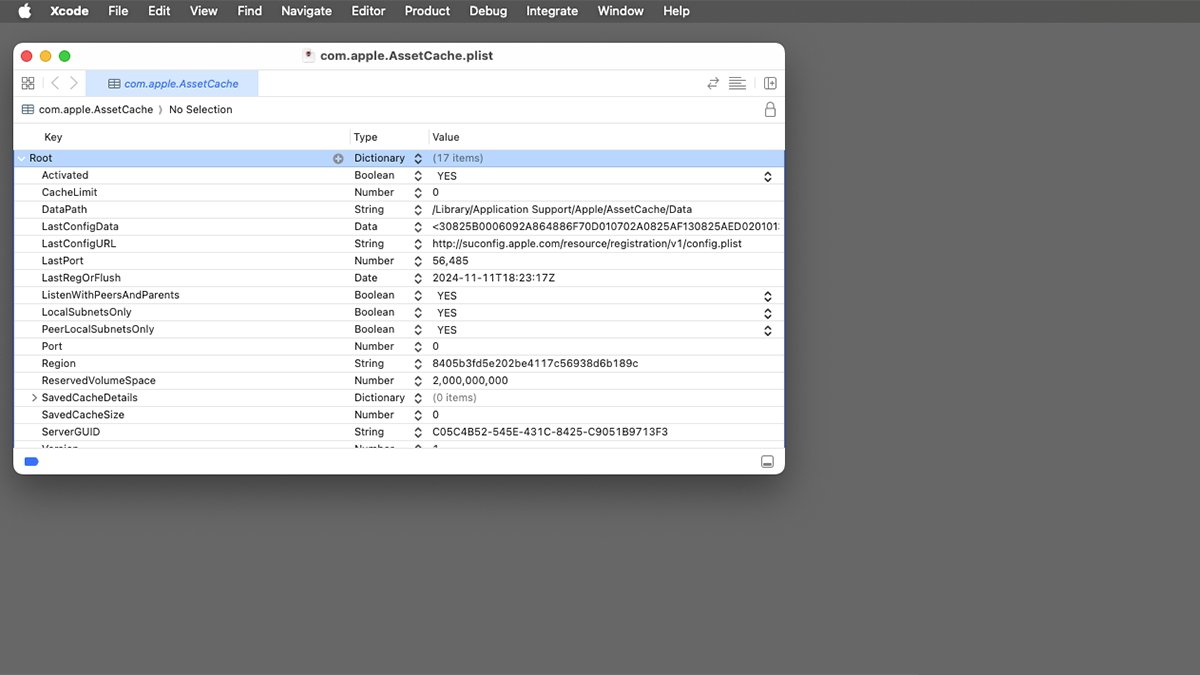
The Mac shops the content material cache settings in a .plist (XML) file at /Library/Preferences/com.apple.AssetCache.plist in your Startup Disk. You possibly can open this file in a textual content editor, or in Apple’s Xcode, to edit its settings.
Apple particularly says solely to vary a number of the settings on this file. The others are off-limits, and in the event you change them, it might trigger your Mac to malfunction or be rendered unusable.
See under for the total listing.
AssetCacheManagerUtil
When you do not wish to edit the settings instantly within the .plist file, you possibly can as an alternative edit them in macOS’s Terminal app through the use of the AssetCacheManagerUtil command-line device.
To get extra information on AssetCacheManagerUtil in Terminal sort:
man AssetCacheManagerUtil and press Return.
You may want to make use of the sudo prefix when utilizing the AssetCacheManagerUtil device.
If you’re executed altering your content material cache settings, drive a reload of the settings through the use of the reloadSettings choice for the AssetCacheManagerUtil device:
sudo AssetCacheManagerUtil reloadSettings
Apple states some values require you to cease after which restart Content material Caching in System Settings.
You can even use the defaults system in Terminal to set easy and superior settings. To view all commonplace content material cache settings in Terminal sort:
sudo AssetCacheManagerUtil settings and press Return.
XML
For extra complicated instructions you will have to know how you can use the defaults system in Terminal, and how you can write XML (Extensible Markup Language) to go parameters to the defaults system.
XML is actually key-value pairs saved in plain textual content, which may be nested with information separated by commas and curly braces.
For instance, '( { first = 10.0.0.1; final = 10.0.0.254; }, { first = 10.1.0.1; final = 10.1.0.254; } )' incorporates an array of two keyed dictionaries with first and final keys set to totally different web addresses.
XML is definitely pretty straightforward to jot down and perceive as soon as you know the way the syntax and nesting works. XML is extensively used all around the web to go and retailer information, however extra not too long ago has been outdated by JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). A dictionary is only a set of key/worth pairs bundled collectively for simple entry.
AssetCacheManagerUtil can output its information in JSON format utilizing the -j choice however defaults typically makes use of XML because it older.
Which values to vary
A few of the values in com.apple.AssetCache.plist have to be clamped between two allowable values. Do not change these to something exterior their allowed ranges.
By altering these values you possibly can alter numerous how the content material cache behaves together with timeouts, limits on how huge the cache may be, disk area, alerts, and extra.
You can even set the verbosity stage of the cache logs if you would like extra details about the way in which it behaves.
By altering these settings you possibly can management and alter how your Mac shops, masses, deletes, and shares content material caches.
Additionally see the part Arrange content material caching on Mac within the Mac Person Information.